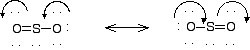|

Rasmol colors are used in the exercise. In the jmol menu bar click
on Options and rasmolColors. To check atom: either put the screen cursor
on the atom, or click on Console, then click open, and then click the
atom.
|
|
[Organic Molecules Worksheet (1)]
Click on the active link in each of the squares above for a molecule's
image (lone pairs of electrons are not in the images). The images must
be manipulated in order to get an accurate view of the molecules; not all of
the atoms will be visible without doing so. Complete the table provided to you;
for each image: 1) Write
the molecular formula for the molecule. 2) Identify the number of
valence electrons for each atom in the molecule and the total number of
electrons for the complete molecule. 3) Draw a Lewis structure that
represents the molecule, 4) Describe the shape of the molecule,
and to the best of your ability indicate if you think that molecule is
polar or non-polar.
For example, 4A:
SO2, S=6, O=6, SO2=18, bent shape, polar: see handout
for the Lewis structure.
Resonance:
Using the jmol bond length feature, check the respective bond lengths
for 4A:
SO2, by double clicking on the sulfur atom and then each respective
oxygen atom. The Web model has equal bond lengths (1.565 Angstroms,
0.1565 nm) for both sulfur to oxygen bonds, despite a Lewis structure which
shows an S-O single bond that is >1.57 Angstroms (Å), and an S=O
double bond that is < 1.57 Angstroms (Å). The two possible Lewis
structures for SO2. are shown below. In one case there
is a single bond on the right, double on the left, and in the other case
a double bond on
the right and a single
bond on the left.
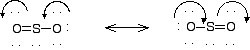
The actual, net result is a weighted average of the two.
In this case, the Sulfur-Oxygen bond is a double bond about 50% of
the
time and a single bond about 50% of the time.
Draw 3 different Lewis structures for the polyatomic carbonate ion CO32-
using arrows to show the electron movements between the three structures.
(The 2- charge indicates that there are 2 additional electrons in the ion.)
Check the bond lengths with jmol and record the bond length values in Angstroms
(Å) for the respective bonds. Repeat the steps for the acetate ion.
Consider that a pure C-O single bond is about 1.40 Å, and a pure
C=O double bond is about 1.20 Å. Briefly describe the bond character
of the Carbon-Oxygen bonds in the respective polyatomic ions.
Draw Lewis structures for methanol, diethyl ether, formaldehyde,
acetone, and acetic acid.